- 10 June 2010
- Posted by: nemcatgroup
- Category: Publications
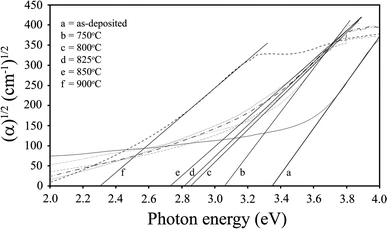
Essentially fully dense titania thin films were spin coated on fused quartz substrates under identical conditions and subjected to annealing over the range 750°–900°C. The films were of a consistent ~400 nm thickness. The anatase → rutile phase transformation temperature was between 750°C and 800°C, with first-order kinetics; annealing at 900°C yielded single-phase rutile. Silicon contamination from the fused quartz substrate was considered to be critical since it suppressed both titania grain growth (maintaining constant grain size) and the phase transformation (occurring at an unusually high temperature); its presence also was considered to be responsible for the formation of lattice defects, which decreased the transmittances and the band gaps.
