- 1 November 2022
- Posted by: nemcatgroup
- Category: Publications
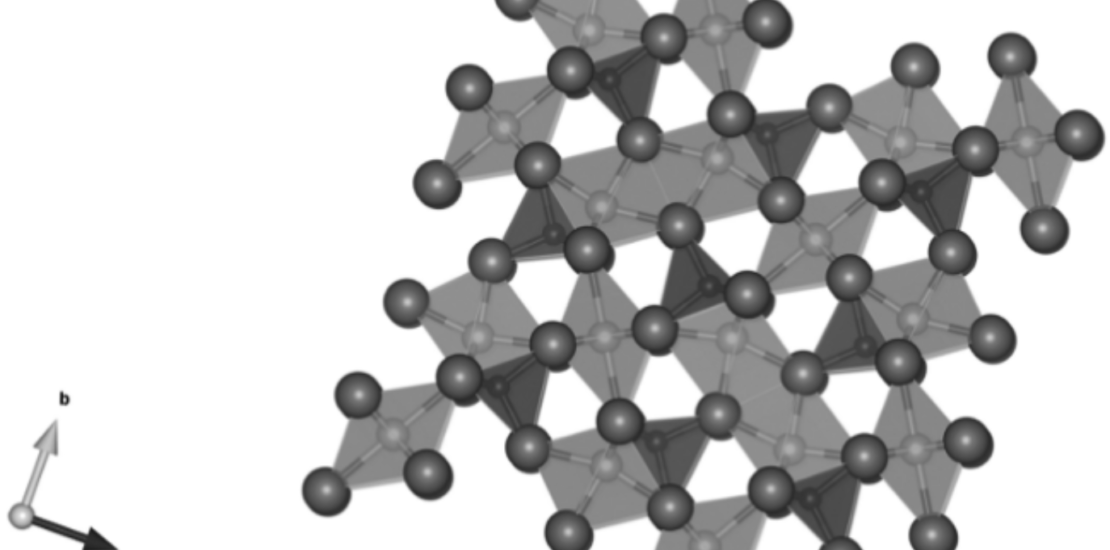
Mullite (3Al2O3·2SiO2) is an aluminosilicate that displays several advantageous mechanical, optical, and thermal properties, which have enabled its application in a wide range of industries in pure and composite forms. Mullite-based composites are composed of a mullite matrix with reinforcements of typically alumina (Al2O3), zirconia (ZrO2), and/or silicon carbide (SiC), and in some cases, mullite itself, in the form of particles, fibres, and/or whiskers. The goal of these additions is to improve the mechanical and thermal properties of the composites. However, understanding the impact of these secondary phases on the mechanical property requires elucidation of the nature of the reinforcement and their interactions with the matrix, their effects on relevant toughening mechanisms, and the critical role of the processing route. This review provides relevant information on mullite, mullite-based composites, and composite fabrication methodologies and discusses the effects of different ceramic reinforcement materials on the toughening mechanisms in these composites. The mechanisms are closely linked to the microstructural features, processing conditions, and form and amount of the secondary phases. The addition of ceramic fibre reinforcement appears to be the most promising option to improve the fracture toughness with additional enhancement obtained by coating the fibres to cause interfacial debonding.
