- 30 October 2018
- Posted by: nemcatgroup
- Category: Publications
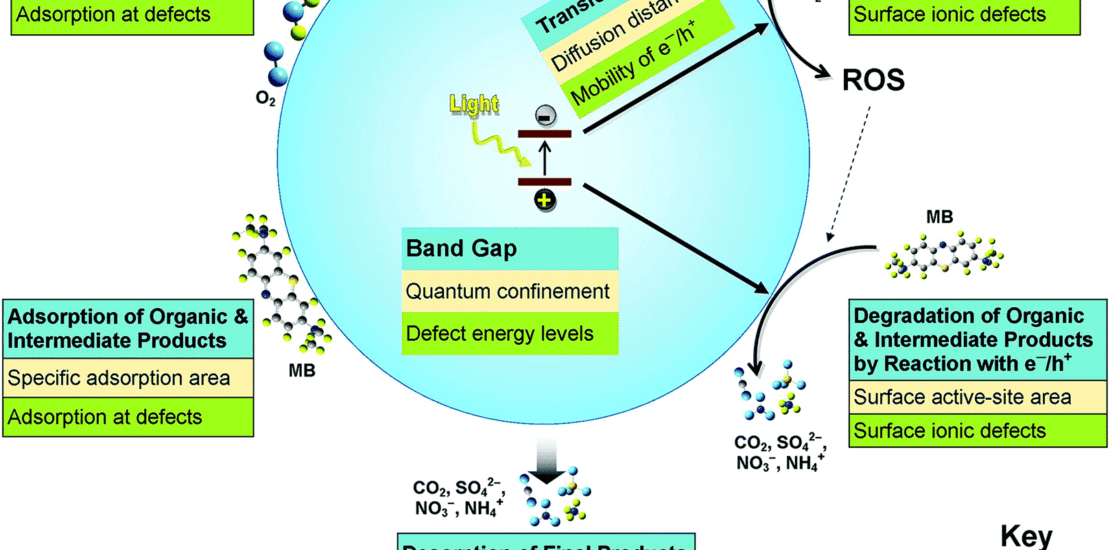
The present work reports data for the mineralogical, nanostructural, optical, and photocatalytic properties of Cr-doped, V-doped, and Cr/V-codoped TiO2 nanoparticles in terms of the effects of doping level and associated particle size on their photocatalytic performance. The photocatalytic performance of doped TiO2 is dependent not only on the particle size at low-doping levels but also on both the type and amount of dopant(s) at high-doping levels. These data illustrate the existence of two clear regimes in behaviour and enable the introduction of a new interpretation of the causes of these effects. At ultralow and low-doping levels, extrinsic effects (viz., particulate characteristics) determine the performance. At high-doping levels, intrinsic effects (viz., dopant-controlled chemical and electrical characteristics) determine the performance. In the intermediate range of medium-doping levels, the performance shows the mixed effects of these two factors. A schematic model comprehensively summarizing the role of doping in these extrinsic and intrinsic effects on the photocatalytic process is presented. Further, a phenomenological model that identifies the regions of dominance of these effects as a function of particle size and doping level on the photocatalytic performance is proposed. These generic models assist in both understanding the systematic effects of doping on photocatalysts and identifying approaches for modification.
