- 1 February 2016
- Posted by: nemcatgroup
- Category: Publications
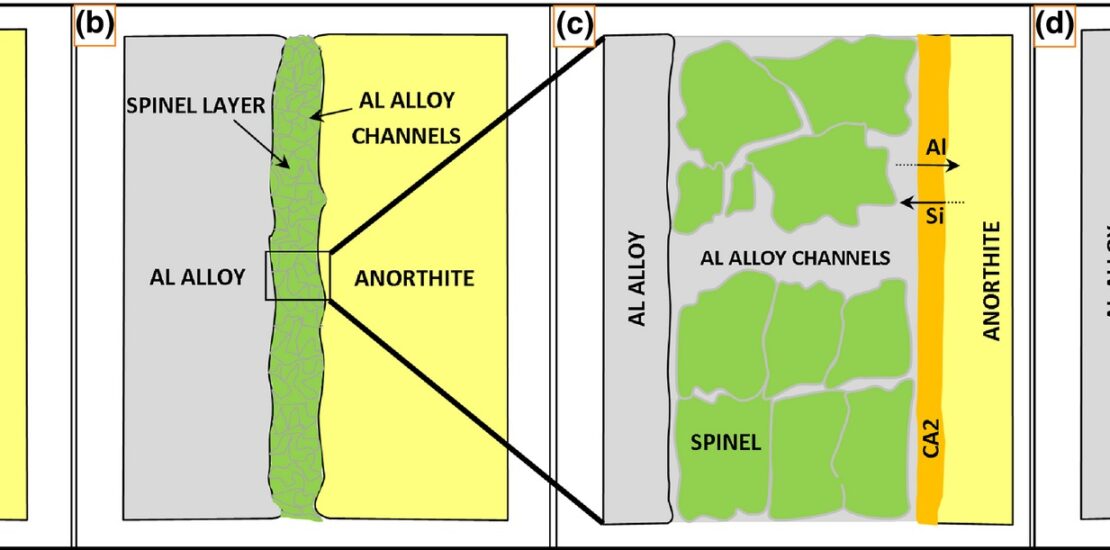
The present work reports an investigation of the interactions of Al 7075 alloy and anorthite at 850°C (150 h) and 1150°C (24 h). Transmission electron microscopy, electron probe microanalysis, X-ray diffraction, and scanning electron microscopy coupled with energy-dispersive spectroscopy were used to identify the mineralogical and microstructural changes at the metal–ceramic interface. At 850°C, the phase formation mechanisms were (a) Si4+–Al3+ interdiffusion between the Al alloy and anorthite to form calcium dialuminate (CA2) and Ca2+–Mg2+ interdiffusion between the Al alloy and calcium dialuminate to form spinel. At 1150°C, spinel + Al2O3 and calcium hexaluminate (CA6) + CA2 were the major and minor phase mixtures, respectively in the corroded area. A thin layer of calcium monoaluminate (CA), gehlenite, and Si was present in the immediate vicinity of anorthite. The early stages of corrosion at 1150°C and 850°C were identical. However, due to thickening of the corroded region (viz., spinel formation) and enhanced evaporation of Mg at the higher temperature, the interdiffusion path evolves from Si4+–Al3+ + Ca2+–Mg2+ to Si4+–Al3+ + Ca2+–Al3+, thus establishing the following phase evolution path at the interface:
