- 25 January 2012
- Posted by: nemcatgroup
- Category: Publications
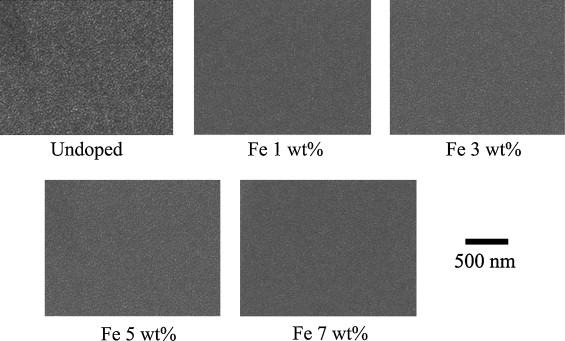
Iron-doped titanium dioxide thin films were coated on fluorine-doped tin oxide coated glass using the spin coating technique. The concentration of the dopant was varied up to 7 mol% iron (metal base). The films were characterised for their structural, morphological, and optical properties. Glancing angle X-ray diffraction and laser Raman microspectroscopy indicate that the films consisted solely of the anatase polymorph of titanium dioxide, without any contamination phases, such as iron oxide. Field emission scanning electron microscopy indicates that the films were microstructurally homogeneous and fully dense, with grains in the size range of ∼10–20 nm. UV-VIS spectrophotometry shows that the optical indirect band gap of the films decreased with increasing iron doping (3.36 eV for undoped and 2.95 eV for 7 mol% Fe).
