- 13 June 2024
- Posted by: nemcatgroup
- Category: Publications
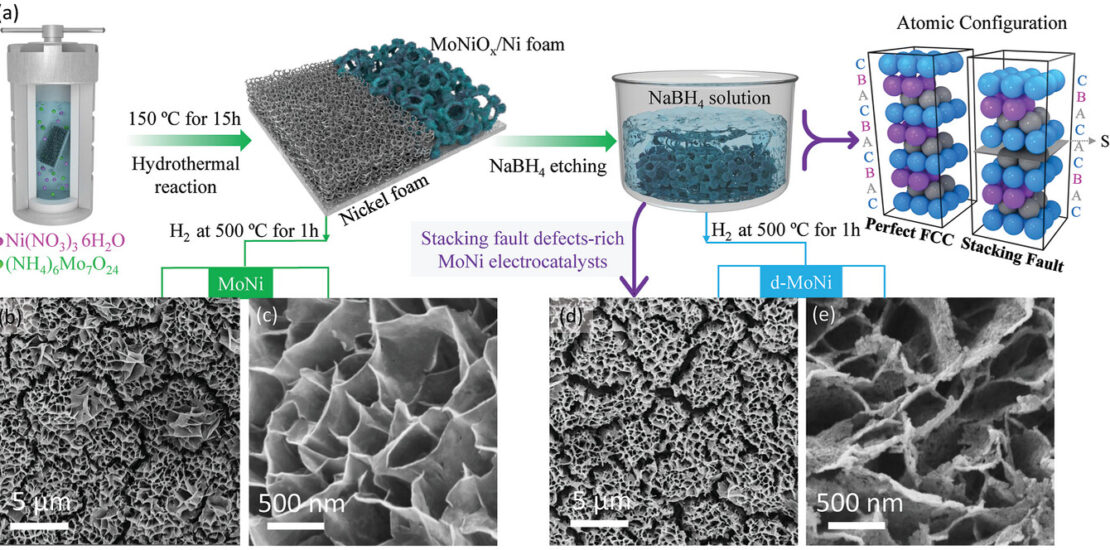
Producing green hydrogen in a cost-competitive manner via water electrolysis will make the long-held dream of hydrogen economy a reality. Although platinum (Pt)-based catalysts show good performance toward hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), the high cost and scarce abundance challenge their economic viability and sustainability. Here, a non-Pt, high-performance electrocatalyst for HER achieved by engineering high fractions of stacking fault (SF) defects for MoNi4/MoO2 nanosheets (d-MoNi) through a combined chemical and thermal reduction strategy is shown. The d-MoNi catalyst offers ultralow overpotentials of 78 and 121 mV for HER at current densities of 500 and 1000 mA cm−2 in 1 M KOH, respectively. The defect-rich d-MoNi exhibits four times higher turnover frequency than the benchmark 20% Pt/C, together with its excellent durability (> 100 h), making it one of the best-performing non-Pt catalysts for HER. The experimental and theoretical results reveal that the abundant SFs in d-MoNi induce a compressive strain, decreasing the proton adsorption energy and promoting the associated combination of *H into hydrogen and molecular hydrogen desorption, enhancing the HER performance. This work provides a new synthetic route to engineer defective metal and metal alloy electrocatalysts for emerging electrochemical energy conversion and storage applications.
