- 18 October 2011
- Posted by: nemcatgroup
- Category: Publications
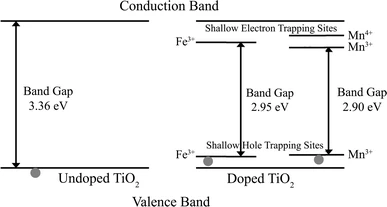
Thin films of TiO2 doped with Fe and Mn were deposited on F-doped SnO2-coated glass by spin coating. Dopant concentrations of 3–7 wt% (metal basis) were used. The structural, chemical, and optical characteristics of the films were investigated. Laser Raman microspectroscopy and glancing angle X-ray diffraction data showed that the films consisted of the anatase polymorph of TiO2. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy data indicated the presence of Fe3+, Mn4+, and Mn3+ in the doped films, as predicted by calculated thermodynamic stability diagrams, and the occurrence of atomic disorder and associated structural distortion. Ultraviolet–visible spectrophotometry data showed that the optical indirect band gap of the films decreased significantly with increasing dopant levels, from 3.36 eV (undoped) to 2.95 eV (7 wt% Fe) and 2.90 eV (7 wt% Mn). These improvements are attributed to single (Fe) or multiple (Mn) shallow electron/hole trapping sites associated with the dopant ions.
