- 1 December 2024
- Posted by: nemcatgroup
- Category: Publications
No Comments
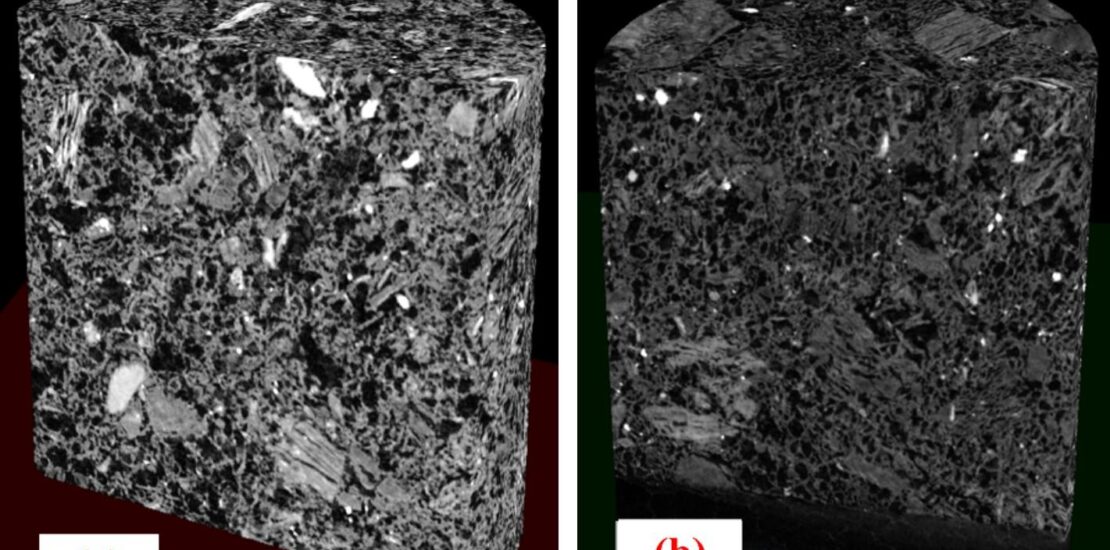
The reduction of CO2 emissions from blast furnace operations is critical to meet decarbonisation targets in the steelmaking sector. Introducing hydrogen gas into the blast furnace displacing pulverised coal or coke is a promising solution to decrease the carbon usage of blast furnace ironmaking because it generates H2O instead of CO2 by reducing the ferrous burden. However, replacing pulverised coal and coke with hydrogen can increase the concentration of H2O and change the thermal and chemical conditions in the furnace. These changes impact the gasification reaction rate and degradation mechanism of coke. In this research, a modified Random Pore Model (RPM) incorporating the processes of internal diffusion and interfacial chemical reaction was developed to investigate the rate and mechanism of coke lump gasification under conditions relevant to conventional and H2-enriched blast furnace conditions. High-temperature thermogravimetric analysis was used to evaluate the gasification of coke lumps with coke reactivity index (CRI) values of 39.5 and 25.3. These experiments were conducted isothermally at temperatures between 1173 K to 1473 K. The results showed that both the diffusion coefficient of the reacting gas and the reaction rate increase with temperature, but these two factors compete to dominate the reaction mechanism. At higher temperatures, the enhanced local carbon reactivity improved conversion near the outer surface of coke lumps. Coke gasification with H2O showed reaction rate constants and effective diffusion coefficients up to 4.7 and 6 times higher, respectively, compared to CO2. Moreover, carbon conversion across the coke lump was more uniform during gasification with CO2 compared with H2O, indicating gasification with CO2 is a chemically controlled process across the temperature range investigated. However, gas diffusion was the dominant mechanism in coke gasification with H2O due to its higher local chemical reaction rate, leading to enhanced carbon conversion near the surface of the lumps.
