- 29 December 2017
- Posted by: nemcatgroup
- Category: Publications
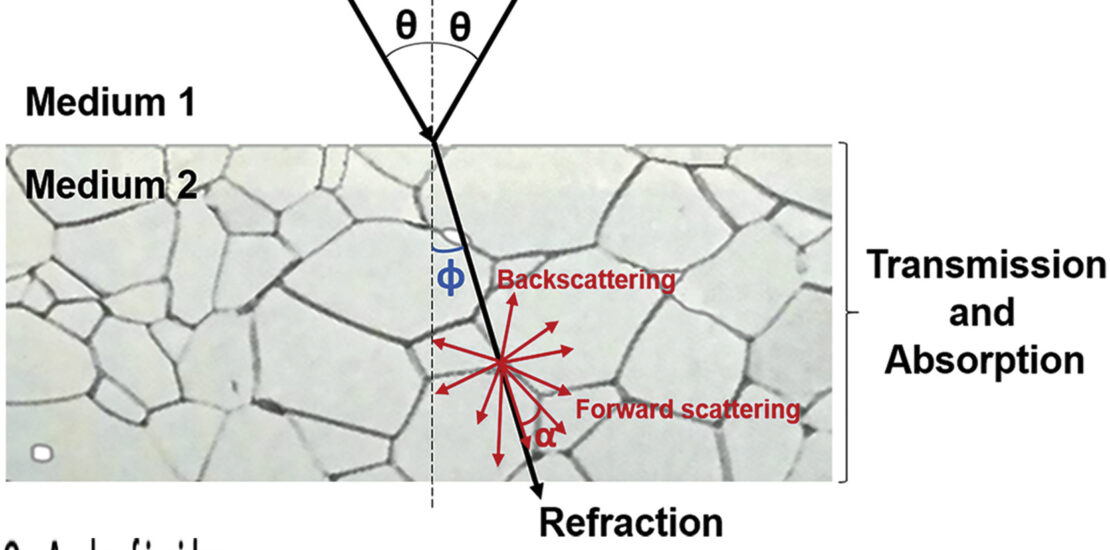
Statement of problem
Yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal has been used as a dental biomaterial for several decades because the fracture toughness and bend strength are increased by a stress-induced transformation-toughening mechanism. However, its esthetics are compromised by its poor translucency and grayish-white appearance.
Purpose
The purpose of the present systematic review was to assess information on the mechanical, chemical, and optical requirements of monolithic zirconia dental restorations.
Material and methods
The following databases (2010 to 2015) were electronically searched: ProQuest, EMBASE, SciFinder, MRS Online Proceedings Library, Medline, Compendex, and Journal of the American Ceramic Society. The search was limited to English-language publications, in vitro studies, experimental reports, and modeling studies.
Results
The data from 57 studies were considered in order to review the intrinsic and extrinsic characteristics of zirconia and their effects on the optical properties.
Conclusions
The materials and microstructural issues relevant to the esthetics and long-term stability of zirconia have been considered in terms of monolithic restorations, while there also are restorations specifically for esthetic applications. Although zirconia-toughened lithium silicate offers the best esthetic outcomes, transformation-toughened zirconia offers the best mechanical properties and long-term stability; cubic stabilized zirconia offers a potential compromise. The properties of these materials can be altered to some extent through the appropriate application of intrinsic (such as, annealing) and extrinsic (such as, shade-matching) parameters.
