- 24 December 2011
- Posted by: nemcatgroup
- Category: Publications
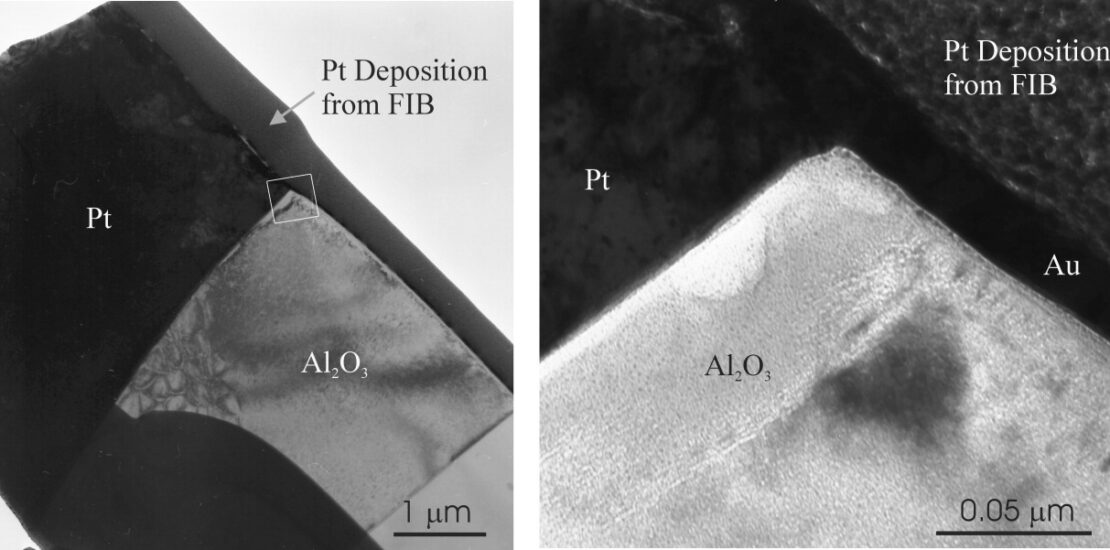
The present work examines the chemistry, microstructure, and crystallography of a Pt-Al2O3 joint used in implantable hermetic feedthrough designs in neural prostheses. Pt was joined to Al2O3 by passing Pt pins through green Al2O3 disks and then sintering in air. This created a Pt-Al2O3 joint that was prepared for the current investigation by gross sectioning and then polishing and sectioning into slices using focused ion beam milling. The slices were examined by scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and energy dispersive spectroscopy. Two types of interfaces in the sintered material were identified: Vitreous-bonded Pt-glass-Al2O3 and direct-bonded Pt-Al2O3. In the case of the former, glass formation owing to the presence of glass-forming additives (to enhance densification and suppress grain growth) and consequent wetting of both the Pt and Al2O3 facilitated interfacial bonding. In the case of the latter, the interfacial planes were (002)Pt // (0  2)
2) [rhombohedral] or (002)Pt // (0
[rhombohedral] or (002)Pt // (0  2 2)
2 2) [hexagonal]. The lattice mismatch was calculated to be 11% (based on the calculated d spacings) or 15% (based on the literature d spacings). Both of these suggest the establishment of semicoherent interfaces.
[hexagonal]. The lattice mismatch was calculated to be 11% (based on the calculated d spacings) or 15% (based on the literature d spacings). Both of these suggest the establishment of semicoherent interfaces.
