- 12 January 2012
- Posted by: nemcatgroup
- Category: Publications
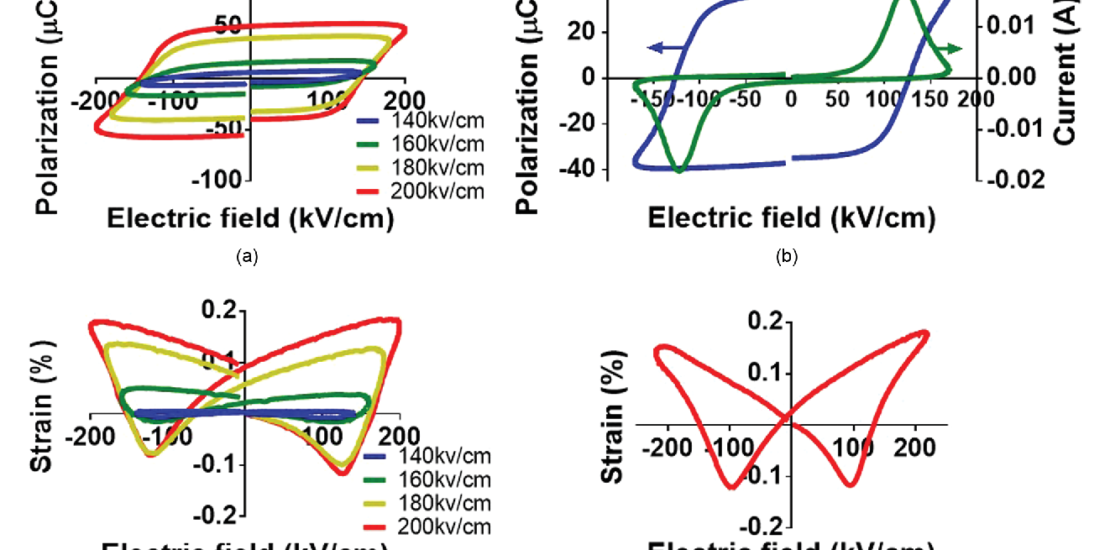
The route to phase-pure BiFeO 3 (BFO) ceramics with excellent ferroelectric and electromechanical properties is severely impeded by difficulties associated with the perovskite phase stability during synthesis. This has meant that dopants and solid solutions with BFO have been investigated as a means of not only improving the functional properties, but also of improving the perovskite phase formation of BFO-based ceramics. The present work focuses on Sm-modified BFO ceramics of composition Bi 0.88 Sm 0.12 FeO 3 . The polarization and strain behaviors were investigated as a function of the phase composition, microstructure, and chemical composition. Addition of Sm reduces the susceptibility of the BFO perovskite to phase degradation by Si impurities. Si was observed to react into Sm-rich grains dispersed within the microstructure, with no large increases in the amount of bismuth-parasitic phases, namely Bi 25 FeO 39 and Bi 2 Fe 4 O 9 . These as-prepared ceramics exhibited robust polarization behavior showing maximum remnant polarizations of ~40 to 50 μC/cm 2 . The electric-fieldinduced strain showed an appreciable stability in terms of the driving field frequency with maximum peak-to-peak strains of ~0.3% and a coercive field of ~130 kV/cm.
